Understanding Private Practice Psychiatrists: A Comprehensive Guide
The field of psychiatry plays an important role in mental health care, providing assessments, medical diagnoses, and treatments for numerous mental health disorders. While lots of psychiatrists operate in healthcare facilities or clinics, private practice psychiatrists provide a special perspective and method to mental health treatment. This article explores the responsibilities, advantages, difficulties, and factors to consider for private practice psychiatrists, shedding light on their important contributions to mental health care.
What is a Private Practice Psychiatrist?
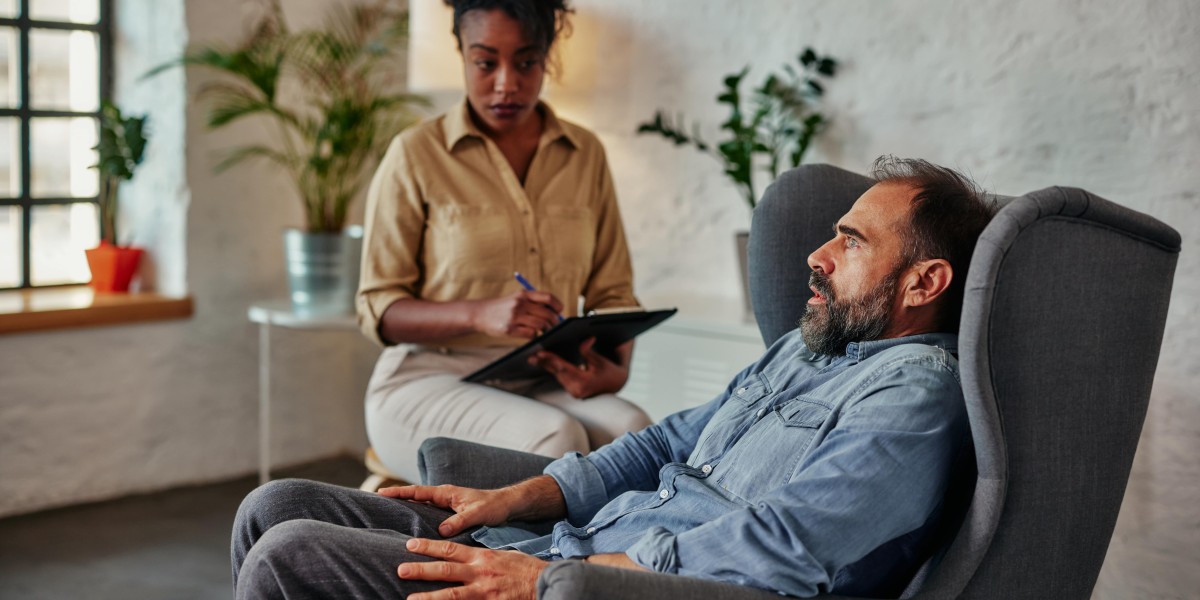
A private practice psychiatrist is a medical physician who concentrates on identifying and dealing with mental health disorders and runs separately. They usually see clients in a workplace setting instead of in a hospital or clinic. This autonomy allows them to produce a customized approach to their practice, typically leading to more powerful therapeutic relationships with customers.
Key Responsibilities
Private practice psychiatrists have a wide variety of obligations, which may include:

- Assessment and Diagnosis: Performing detailed evaluations to diagnose mental health conditions.
- Treatment Planning: Developing individualized treatment plans tailored to the special requirements of each patient.
- Medication Management: Prescribing medications and monitoring their effects, making adjustments as required.
- Psychiatric therapy: Providing therapeutic interventions such as cognitive behavior modification, psychoanalysis, or group therapy.
- Patient Advocacy: Supporting patients in navigating mental health issues, consisting of coordinating with other health care companies.
- Continuing Education: Staying updated with the newest research study and improvements in psychiatry.
Benefits of Private Practice
Private practice uses numerous benefits for psychiatrists, consisting of:
- Autonomy: Control over their practice environment, treatment approaches, and work schedule.
- Personalized Care: The ability to develop stronger relationships with clients, resulting in more tailored treatment strategies.
- Versatile Work Environment: The choice to pick the hours they work and the clients they see.
- Financial Independence: Potential for greater earnings due to direct billing and flexible prices.
Challenges of Private Practice
Despite its benefits, private practice likewise provides a number of challenges:
- Administrative Responsibilities: Managing billing, insurance claims, and office administration can be time-consuming.
- Seclusion: Working independently can be lonely, as there might not be coworkers on-site for immediate assessment or support.
- Client Acquisition: Relying on marketing and networking to attract and maintain patients can be tough and competitive.
- Financial Risks: The requirement for self-funding at the start and the risk of varying earnings due to patient volume.
Factors To Consider for Aspiring Private Practice Psychiatrists
For those considering a career in private practice psychiatry, the following elements ought to be examined:
- Educational Requirements: Aspiring psychiatrists need to finish medical school followed by a residency in psychiatry, which can take around seven years post-undergraduate research studies.
- Licensure: Psychiatrists need to get a license to practice psychiatry in their state and might likewise pursue board certification.
- Comprehending Market Needs: Evaluating the need for psychiatric services in the area assists determine prospective client populations.
- Service Skills: Knowledge of business management, consisting of marketing and financing, is important in running an effective practice.
Normal Patient Profiles
In private practice, psychiatrists may experience a range of clients with differing mental health needs. Below are some common patient profiles:

- Adults with Anxiety Disorders: Generalized anxiety condition, panic attack, social stress and anxiety disorder.
- People with Mood Disorders: Major depressive disorder, bipolar affective disorder, seasonal affective condition.
- Children and Adolescents: Issues such as ADHD, anxiety, and behavioral problems.
- Patients Seeking Medication Management: Individuals who require continuous medication for chronic mental health conditions.
FAQs about Private Practice Psychiatry
Q1: How do I find a private practice psychiatrist?
A1: You can ask for referrals from primary care medical professionals, search online directory sites, or examine with regional mental health companies. It's also a good idea to search for psychiatrists who are board-certified.
Q2: What types of insurance coverage do private practice psychiatrists accept?
A2: Many private practice psychiatrists accept various insurance coverage strategies. It's crucial to ask about accepted plans before scheduling a consultation.
Q3: How long are normal treatment sessions?
A3: Therapy sessions typically last 45 to 60 minutes, although it can differ based on the psychiatrist and the treatment plan.
Q4: Can private practice psychiatrists offer telehealth services?
A4: Yes, many private practice psychiatrists use telehealth services, enabling clients to get care from another location through video conferencing.
Private practice psychiatry represents a devoted sphere within mental health care that combines medical competence with personalized client interaction. While it supplies lots of advantages, including autonomy and personalized treatment, it also features its reasonable share of obstacles. Hopeful psychiatrists must weigh these factors to consider to make informed profession decisions. As mental health continues to gain value in society, the function of private practice psychiatrists will stay essential in dealing with the diverse needs of clients.
Summary Table
| Element | Information |
|---|---|
| Autonomy | Control over practice and schedule |
| Personalized Care | Tailored treatment approaches |
| Financial Independence | Possibly greater earnings |
| Difficulties | Administrative tasks and isolation |
| Normal Patient Profiles | Grownups with stress and anxiety, mood disorders, children with ADHD |
| Insurance Considerations | Varies by provider |
By welcoming the intricacies and rewards of private practice psychiatry, specialists can provide considerable contributions to the mental health landscape while also accomplishing individual and professional fulfillment.